Computer Science Technology: Definition, Key Fields, and Real-World Uses explains what computer science actually covers, why it matters for individuals and businesses, and how it turns ideas into real products—like mobile apps, websites, AI tools, and secure business systems (in Jordan, the GCC, and beyond).
What is computer science technology?
Computer science technology is the study of how computing systems work and how to use them to solve problems efficiently. It includes both:
-
Theory: algorithms, data structures, computation, and how systems process information
-
Practice: software engineering, databases, networks, cybersecurity, and building real applications
In simple terms: it’s the field that powers software, apps, websites, cloud platforms, and intelligent systems.
Why studying computer science matters
Computer science is important because it enables modern services to exist and scale reliably. It helps people and organizations:
-
Build digital products (apps, platforms, websites, systems)
-
Automate repetitive work (faster operations with fewer errors)
-
Make better decisions using data (analytics and forecasting)
-
Improve security and privacy (protect users and business assets)
-
Innovate faster (turn concepts into deployable solutions)
Key fields inside computer science technology
Software engineering
How software is designed, built, tested, deployed, and maintained.
What it includes
-
clean architecture, code quality, version control (Git)
-
testing strategies and release processes
-
maintainability and scalability
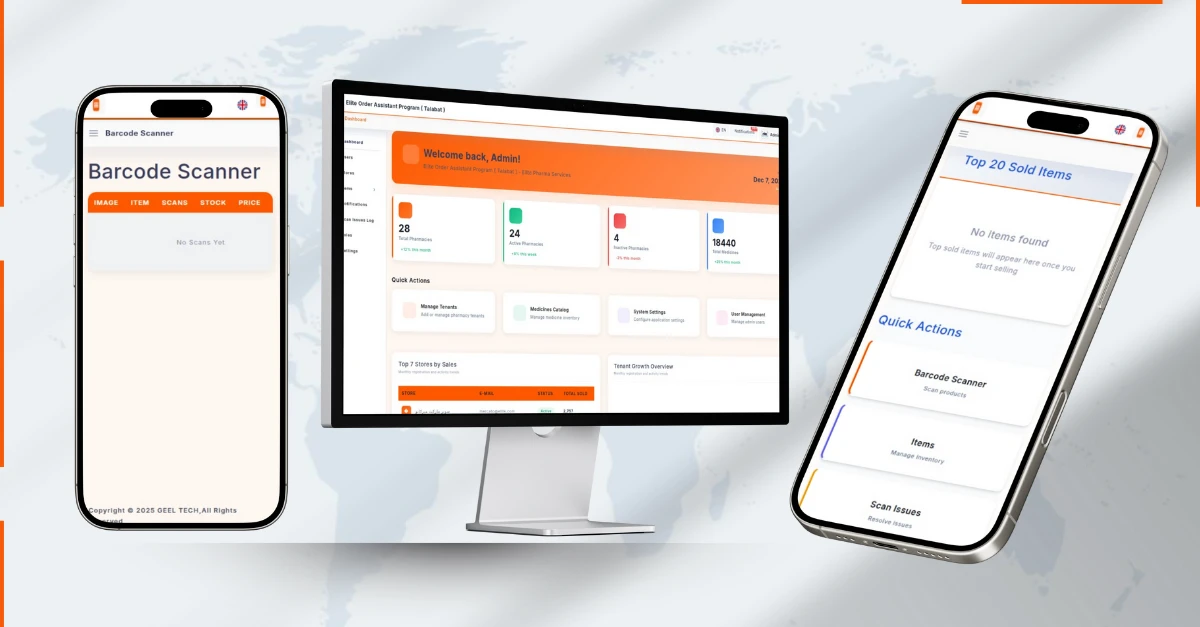
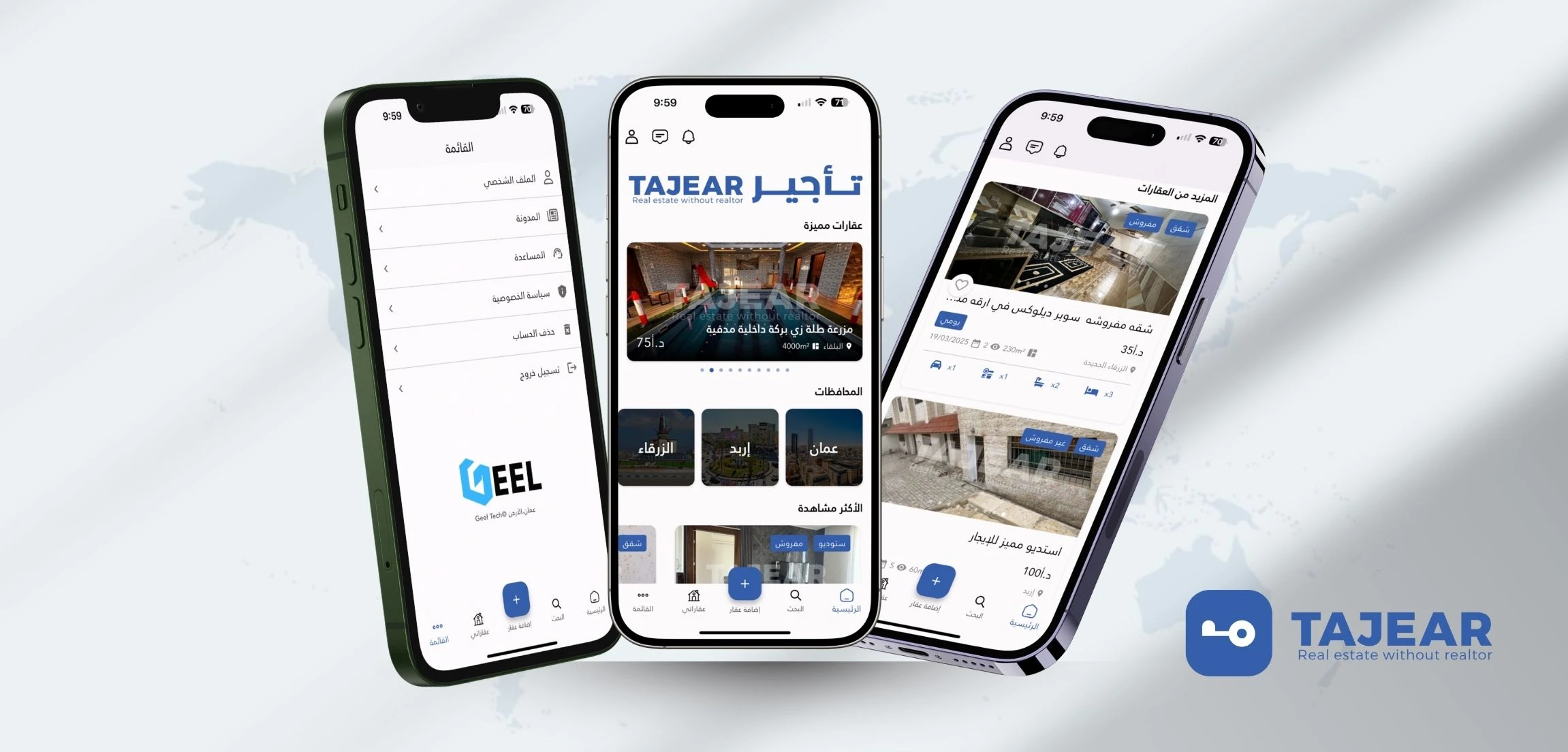
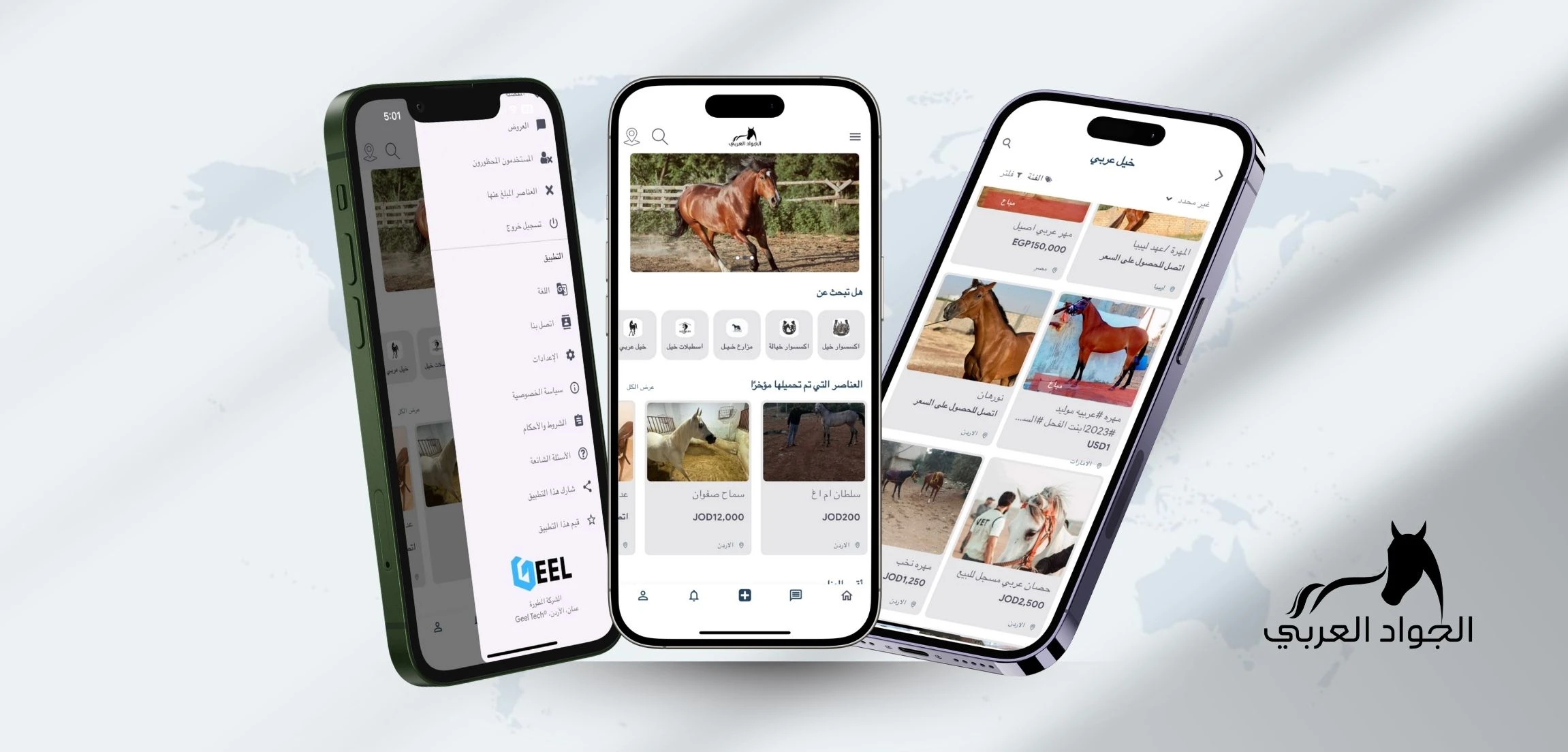
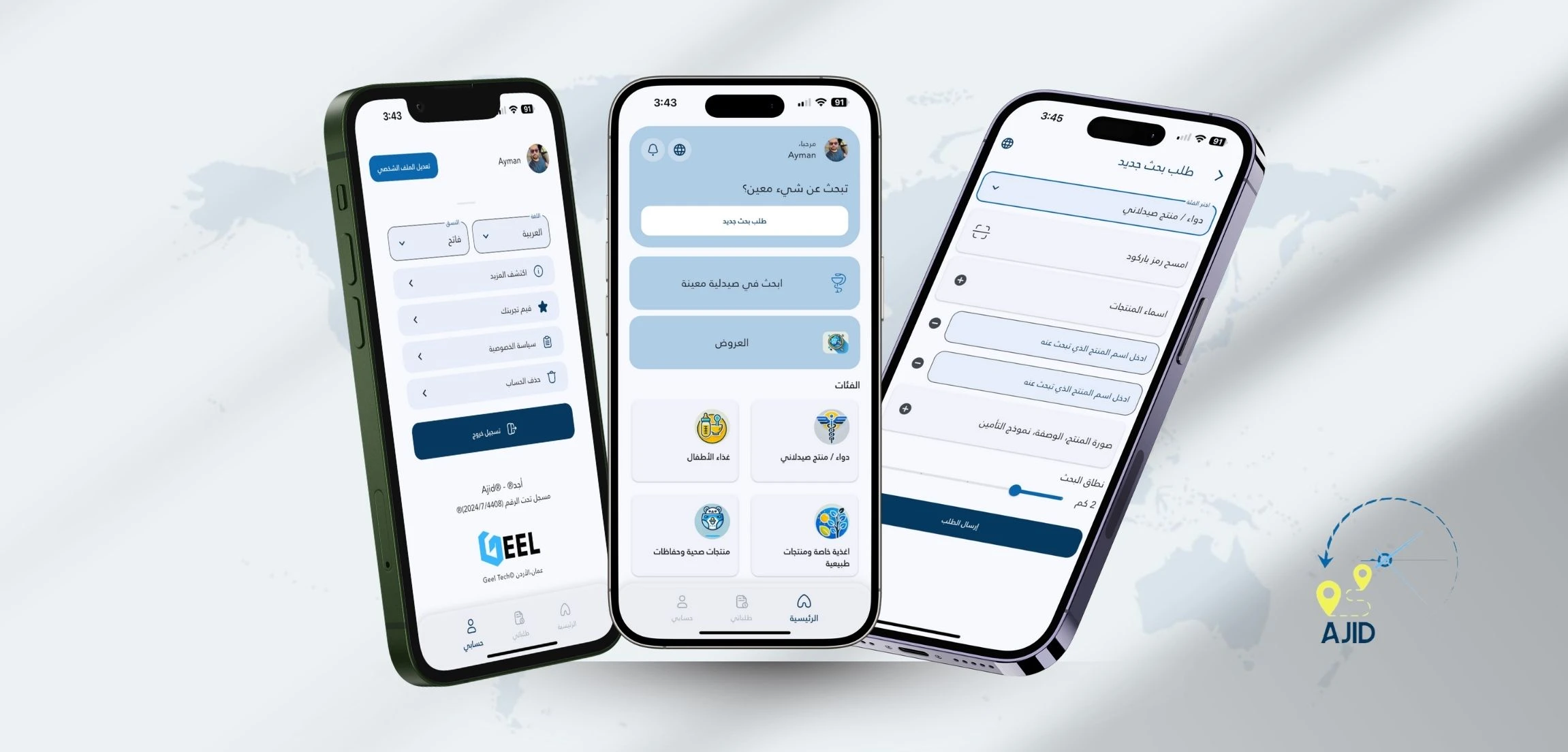
Mobile app development (Android/iOS)
Building mobile apps for smartphones and tablets.
What it includes
-
Android (Kotlin) and iOS (Swift), or cross-platform (Flutter/React Native)
-
app performance, device permissions, offline/weak network handling
-
app store publishing and updates
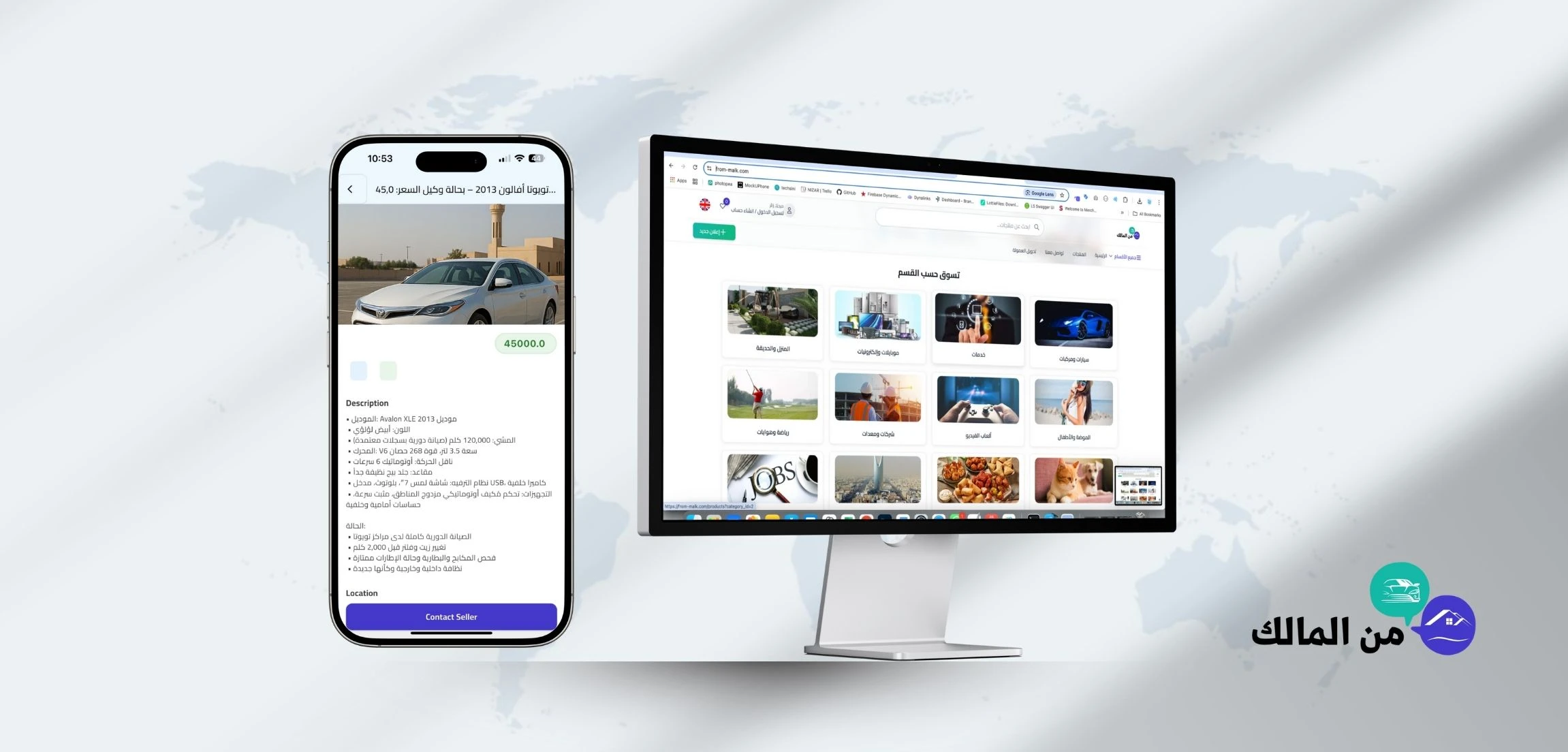
Web development
Building websites and web applications people use through browsers.
What it includes
-
front-end (UI), back-end (APIs), and databases
-
performance optimization and security
-
admin dashboards and business portals
Databases and data systems
How data is stored, organized, and retrieved reliably.
What it includes
-
relational databases (MySQL/PostgreSQL)
-
data modeling and reporting
-
data quality and consistency
APIs and integrations
How systems communicate with each other.
What it includes
-
REST/GraphQL APIs
-
authentication, permissions, and secure tokens
-
integrating payments, maps, messaging, ERP/CRM, analytics
AI and data science
Using data to predict, classify, recommend, and automate decisions.
What it includes
-
machine learning and deep learning
-
natural language processing (NLP)
-
evaluation, bias checks, monitoring, and safe deployment
Cybersecurity
Protecting systems and users from threats.
What it includes
-
secure authentication and access control
-
encryption, vulnerability management
-
logging, monitoring, and incident response
Skills that matter in real projects
If someone says they “work in computer science,” these are the skills that show up most often:
Core foundations
-
Problem solving and algorithms
-
Data structures (arrays, trees, graphs—basics that improve performance)
-
System thinking (how parts connect and fail)
Practical build skills
-
Databases and data modeling
-
API design and integration
-
Testing and quality assurance
-
Deployment basics (cloud hosting, environments, monitoring)
Product skills (important for adoption)
-
UI/UX thinking (flows, clarity, accessibility)
-
Performance (speed and stability on real devices)
-
Security mindset (protect users by default)
How computer science connects to real business services (closer to your market)
Many businesses don’t need “computer science” as a concept—they need outcomes. Here’s how it maps to real deliverables:
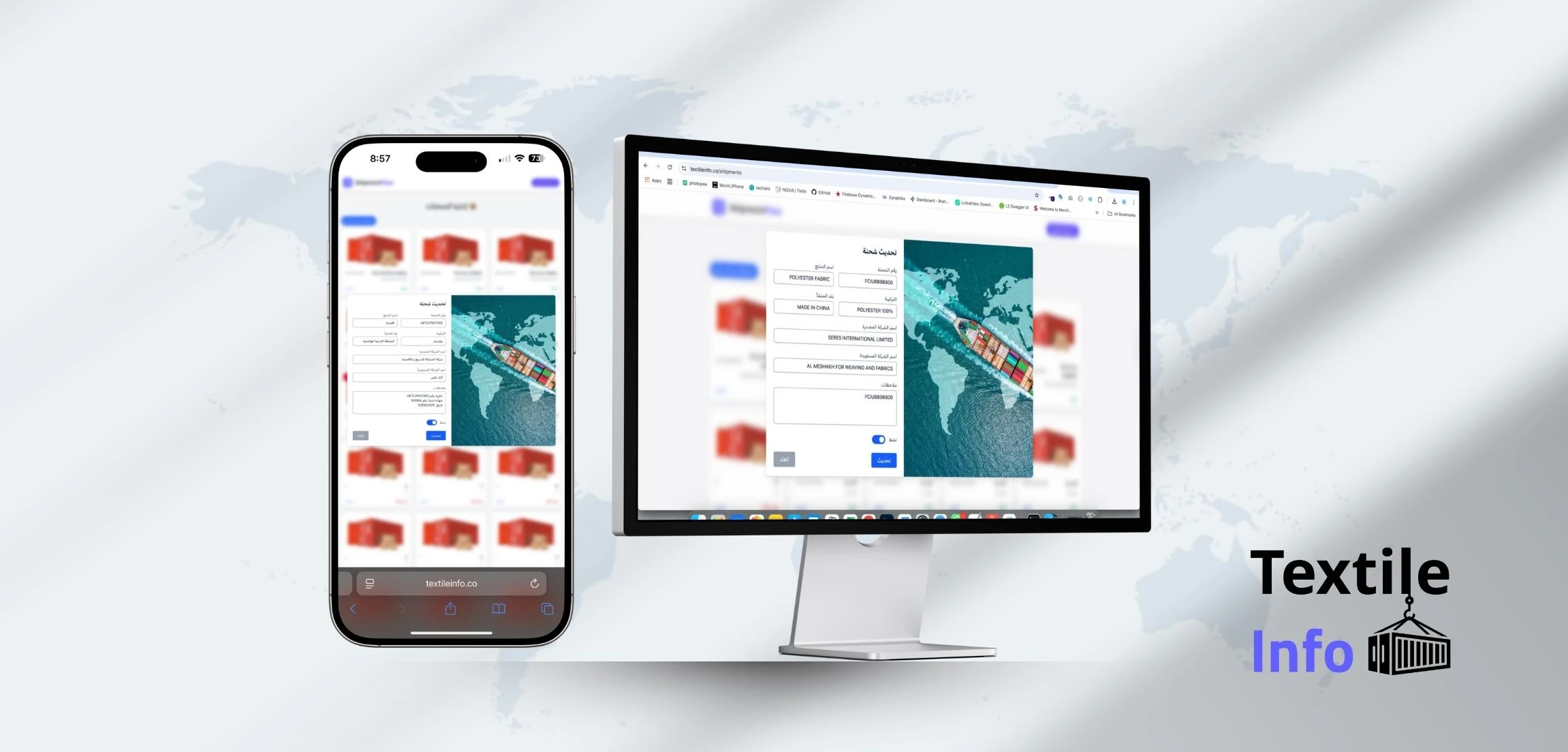
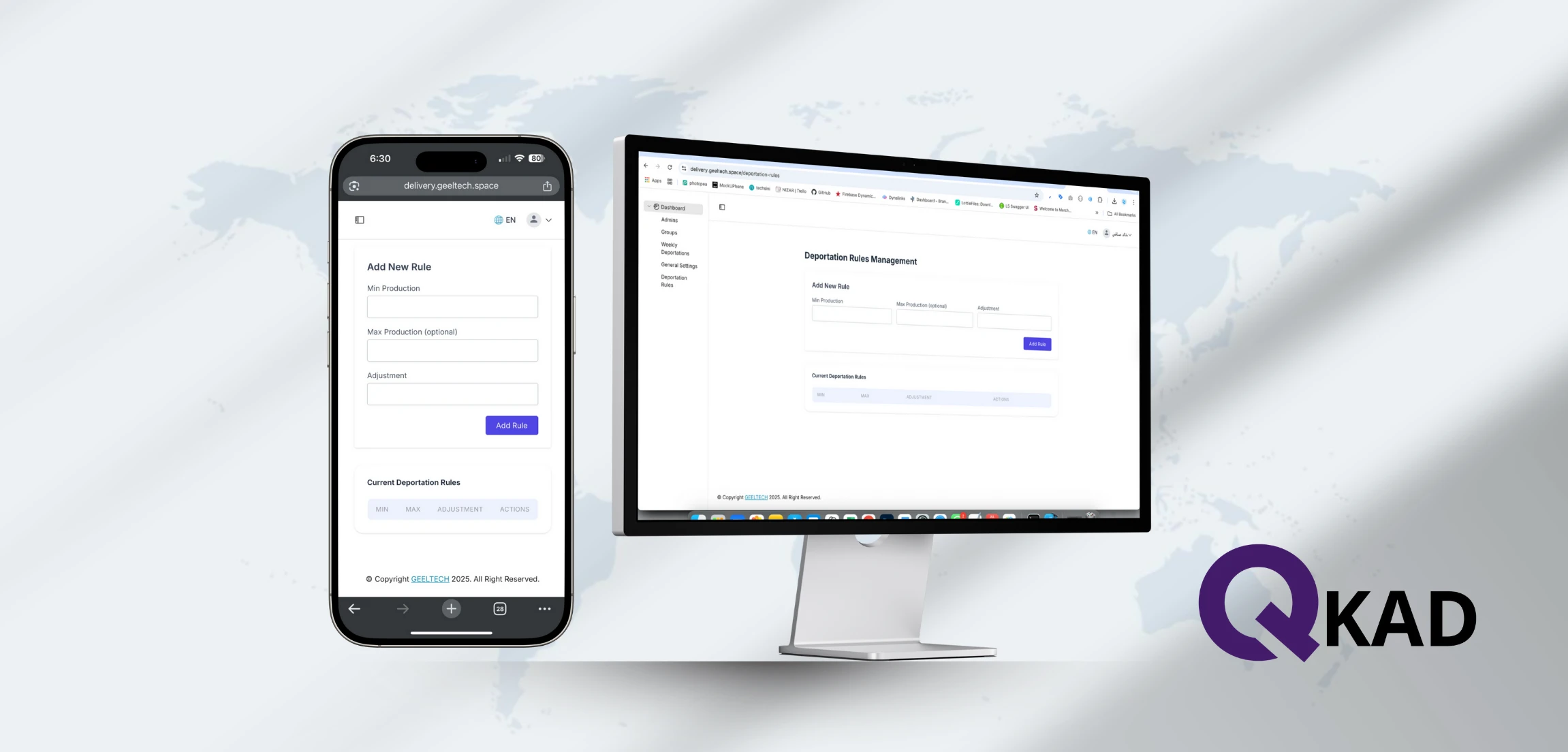
Mobile apps
-
customer apps (ordering, booking, delivery, loyalty)
-
provider/driver apps (tasks, tracking, payouts)
-
admin dashboards (operations, reports)
Websites and platforms
-
corporate websites, landing pages, blogs
-
e-commerce stores and portals
-
internal business systems (HR, inventory, approvals, reporting)
AI features inside products
-
chat assistants for support
-
document automation (invoices, forms)
-
analytics, forecasting, anomaly detection
Security and reliability
-
secure logins and role-based access
-
data protection and audit logs
-
payment and transaction safety
Common misconceptions (quick fixes)
“Computer science is just coding”
Coding is one part. Real computer science also includes architecture, data, security, testing, and system design.
“AI will replace everyone”
AI changes jobs and automates tasks, but most value comes from human + AI collaboration—humans keep accountability, judgment, and responsibility.
“A product is done once it launches”
Modern software needs maintenance: OS updates, security updates, bug fixes, performance improvements, and feature iteration.
FAQ
Is computer science only for people who want to be programmers?
No. It also supports careers in QA/testing, UI/UX product roles (with technical background), data/AI, cybersecurity, DevOps, and technical project roles.
What’s the fastest path to become job-ready?
Start with one track (mobile, web, backend, or QA), build 2–3 real projects, learn APIs + databases, and practice clean release/testing habits.
Why do many software projects fail?
Most failures are not “bad code”—they’re unclear requirements, weak testing, missing monitoring, poor UX, or lack of adoption and training.
How do I connect learning to real market needs in Jordan & GCC?
Focus on business-ready skills: mobile apps, web dashboards, APIs, payments, performance, security, and bilingual UX where relevant.
Conclusion
Computer science technology is the backbone of modern digital life. It powers mobile apps, websites, cloud systems, AI tools, and secure business platforms. When you understand its key fields—software engineering, data, APIs, AI, testing, and security—you can build solutions that work reliably in the real world.
Explore our services: Mobile App Development • Website Design & Development • Custom Software Development


.webp)